Let more growers get greater benefits
SCU vs PCU Urea: Key Differences in Controlled-Release Fertilizers
- Industry News
- December 17, 2016
- 9:58 am
Conventional urea dissolves rapidly after application, often leading to significant nitrogen losses through ammonia volatilization (NH₃), nitrate leaching (NO₃⁻), and denitrification (N₂O). These losses reduce nitrogen use efficiency (NUE), increase fertilization frequency, and raise environmental concerns.
Controlled-release urea (CRU) technologies were developed to synchronize nitrogen availability with crop demand. Among them, SCU (Sulfur-Coated Urea) and PCU (Polymer-Coated Urea) represent two fundamentally different technical pathways, widely used in agriculture, turf management, and horticulture.
As a global fertilizer supplier, Risso integrates both economic and high-performance controlled-release solutions to meet diverse agronomic and market needs.
Table of Contents
- 1. What Is SCU UREA (Sulfur-Coated Urea)?1. What Is SCU UREA (Sulfur-Coated Urea)?
- 2. What Is PCU UREA (Polymer-Coated Urea)?2. What Is PCU UREA (Polymer-Coated Urea)?
- 3. Core Differences Between SCU and PCU3. Core Differences Between SCU and PCU
- 4. Agronomic Performance and Environmental Impact4. Agronomic Performance and Environmental Impact
- 5. Cost Structure, ROI, and Commercial Logic5. Cost Structure, ROI, and Commercial Logic
- 6. Application-Based Selection Guide6. Application-Based Selection Guide
- 7. Common Misconceptions and Technical Insights7. Common Misconceptions and Technical Insights
- 8. Final Conclusion: Correct Positioning of SCU and PCU8. Final Conclusion: Correct Positioning of SCU and PCU
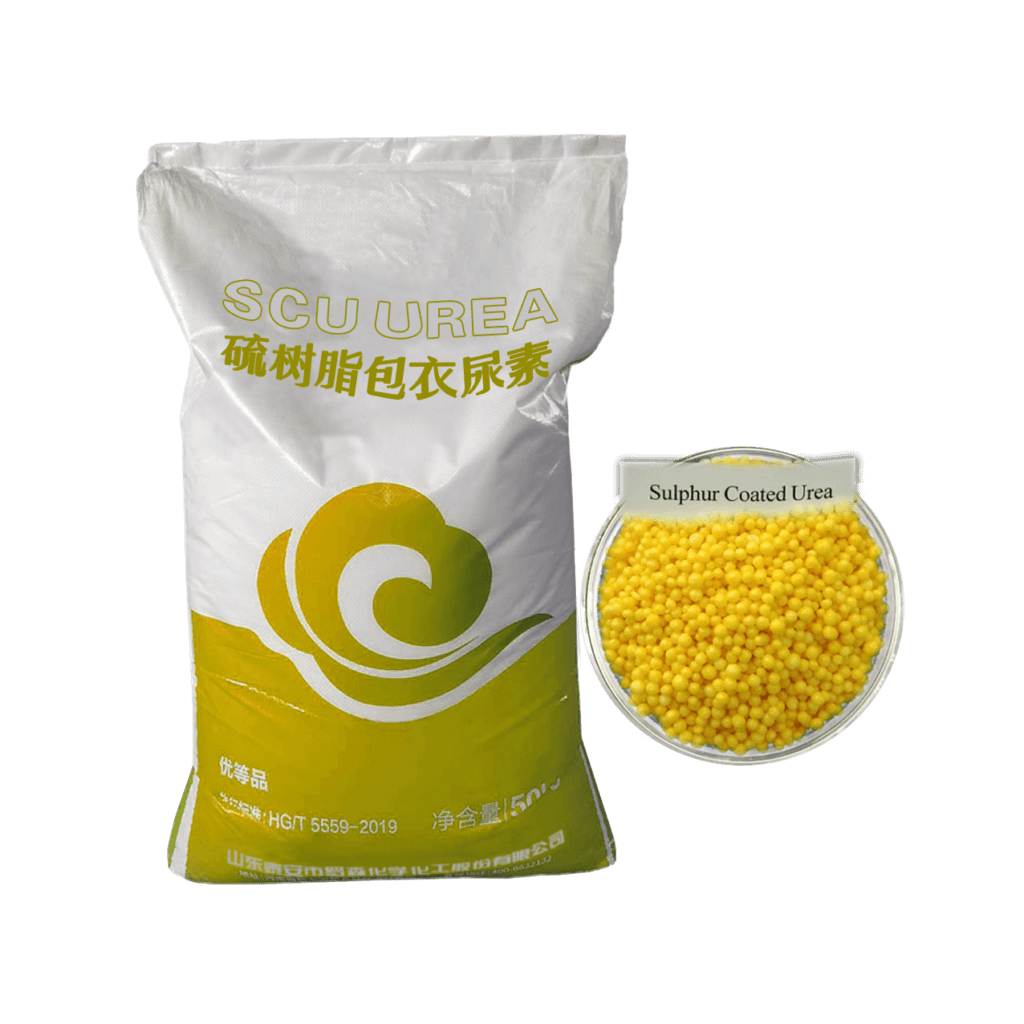
1. What Is SCU UREA (Sulfur-Coated Urea)?
SCU UREA (Sulfur-Coated Urea) is a slow-release nitrogen fertilizer produced by coating urea granules with molten sulfur, often combined with wax or sealants.
1.1 Structure and Composition
- Urea core
- Outer sulfur coating
- Optional wax or hardener sealing layer
1.2 Nitrogen Release Mechanism
- Physical cracking of the sulfur layer during handling or application
- Water penetration through coating defects
- Rapid dissolution of the urea core
- Microbial oxidation of sulfur, further weakening the coating
👉 SCU is best described as an “environment-driven slow-release fertilizer” rather than a precisely controlled one.
1.3 Key Characteristics of SCU
- ✔ Slower nitrogen release than conventional urea
- ✔ Relatively low production cost
- ✔ Provides supplemental sulfur nutrition
- ✖ Release uniformity is limited
- ✖ High sensitivity to moisture, temperature, and mechanical damage
Typical release duration: approximately 6–8 weeks, with considerable variability.
2. What Is PCU UREA (Polymer-Coated Urea)?
PCU UREA (Polymer-Coated Urea) is an advanced controlled-release fertilizer in which urea granules are encapsulated by synthetic or bio-based polymer membranes (e.g., polyurethane or resin systems).
2.1 Structure and Composition
- Urea core
- Single-layer or multi-layer polymer coating
2.2 Nitrogen Release Mechanism (Key Differentiator)
- Soil moisture permeates the polymer membrane
- Urea dissolves inside the capsule
- Nitrogen diffuses outward at a predictable rate governed by membrane thickness, porosity, and temperature
2.3 Key Characteristics of PCU
- ✔ Precisely adjustable nitrogen release rate
- ✔ Smooth, linear release with minimal peak loss
- ✔ Customizable longevity (30, 60, 90, 120–180 days)
- ✔ Significantly improved NUE
- ✖ Higher manufacturing cost
At Risso, PCU technologies are designed to match crop nitrogen uptake curves across different climate zones and cropping systems.
3. Core Differences Between SCU and PCU
3.1 Coating Materials and Physical Structure
| Parameter | SCU | PCU |
|---|---|---|
| Coating material | Sulfur (+ wax) | Polymer (resin / PU) |
| Mechanical strength | Brittle | Elastic and durable |
| Damage resistance | Low | High |
| Release control | Passive | Active |
Interpretation:
PCU coatings provide superior mechanical integrity and release consistency compared to sulfur-based coatings.
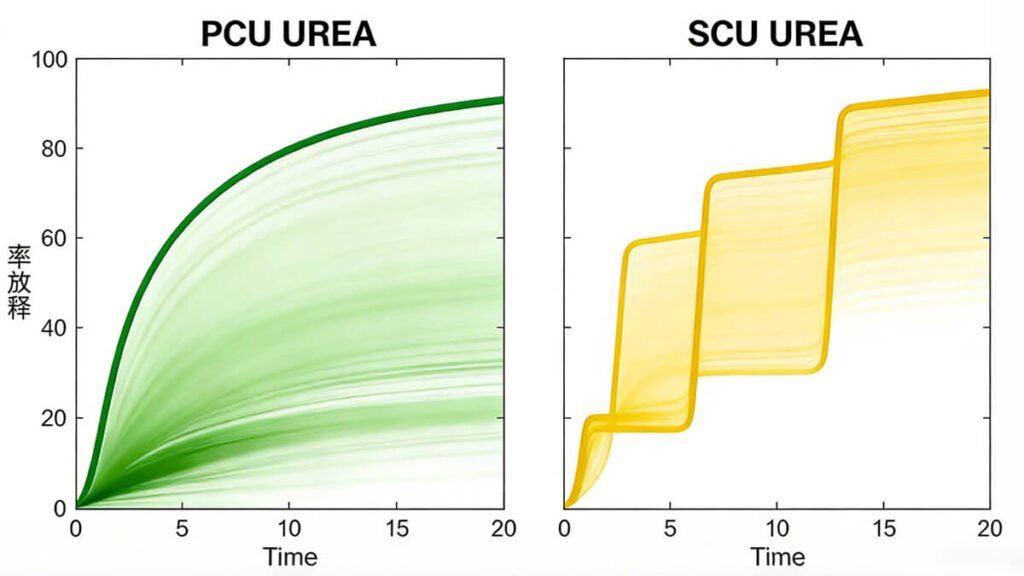
3.2 Fundamental Nitrogen Release Mechanisms
-
SCU:
- Release triggered by coating failure
- High randomness
- Difficult to model accurately
PCU:
- Release governed by diffusion physics
- Predictable and designable
- Closely aligned with crop nitrogen demand
👉 This mechanistic difference explains the performance gap between SCU and PCU.
3.3 Release Duration and Stability
| Performance Metric | SCU | PCU |
|---|---|---|
| Release uniformity | Low | High |
| Risk of nitrogen surge | High | Very low |
| Release period control | Limited | Excellent |
| Customization | Minimal | Strong |
3.4 Environmental Responsiveness
| Factor | SCU | PCU |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature sensitivity | High | Moderate |
| Soil moisture sensitivity | High | Lower |
| Microbial dependency | Moderate | Low |
| Predictability | Poor | High |
4. Agronomic Performance and Environmental Impact
4.1 Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE)
- SCU: Moderate improvement compared with conventional urea
PCU: Significant NUE enhancement, often exceeding 70% under optimized conditions
4.2 Environmental Performance
- SCU: Reduces nitrogen losses relative to uncoated urea
PCU: More effective in minimizing NH₃ volatilization and N₂O emissions, supporting sustainable and low-emission agriculture
| Aspect | SCU | PCU |
|---|---|---|
| Product cost | Lower | Higher |
| Application frequency | Higher | Lower |
| Labor & management cost | Moderate | Lower |
| Overall ROI | Medium | High (for high-value crops) |
💡 Key insight:
Fertilizer decisions should be based on cost per unit of effective nitrogen, not price per ton.

6. Application-Based Selection Guide
🌱 Field Crops
-
Short-season or cost-sensitive crops (corn, wheat):
→ SCU or SCU-based blends High-value or long-season crops (vegetables, orchards, precision farming):
→ PCU preferred
🌿 Turf & Horticulture
- Long-lasting, uniform nitrogen supply is critical
PCU is ideal for premium turf and ornamental applications
🌍 Sustainability-Driven Projects
- Emission reduction and regulatory compliance
PCU offers clear long-term advantages
7. Common Misconceptions and Technical Insights
❌ “SCU and PCU differ only in coating material.”
✅ In reality, they represent two generations of nitrogen release technology.
❌ “Nitrogen content alone determines fertilizer efficiency.”
✅ Release curve shape and NUE are equally critical.
8. Final Conclusion: Correct Positioning of SCU and PCU
- SCU UREA
- Cost-effective slow-release fertilizer
- Suitable for budget-sensitive, short-to-medium duration applications
PCU UREA
- Precision-engineered controlled-release fertilizer
- Ideal for high-value crops, turf, and sustainable agriculture
👉 SCU is an economic solution; PCU is a technological solution.
Rather than competing, they serve different agronomic and commercial tiers.
As a professional fertilizer manufacturer, Risso provides both SCU and PCU solutions to support efficient nitrogen management across global agricultural systems.
Controlled-release urea related products
If you want to know other questions about Controlled-release urea, please contact us and we will provide professional answers.
- Article
What will you get when touch?
✔ Quick & helpful reply within 6 hours.
✔ Tailored solutions for your project.
✔ One-stop product, tech, market
TRENDING
Want to find a China fertilizer manufacturer?
Risso will be your best choice; send us your request for your fertilizer details requirement
TAIAN RISSO CHEMICAL FERTILIZER CO.,LTD.
- Address: High-tech Development Zone, Taian City, Shandong Province
© Copyright 2017 RISSO CHEMICAL. All Rights Reserved.











