Let more growers get greater benefits
Instructions on NPK Fertilizer: A Professional Guide
- Industry News
- May 25, 2017
- 10:35 am

NPK fertilizers play a vital role in enhancing plant growth and agricultural productivity. There are many types of NPK fertilizers, and which types of NPK fertilizer to choose depends on factors such as soil type, crop needs, and growth stage.
This comprehensive guide provides detailed instructions for effectively using NPK fertilizers, ensuring that your plants receive balanced nutrition tailored to their specific needs.
List of Contents
1. Understanding NPK Ratios
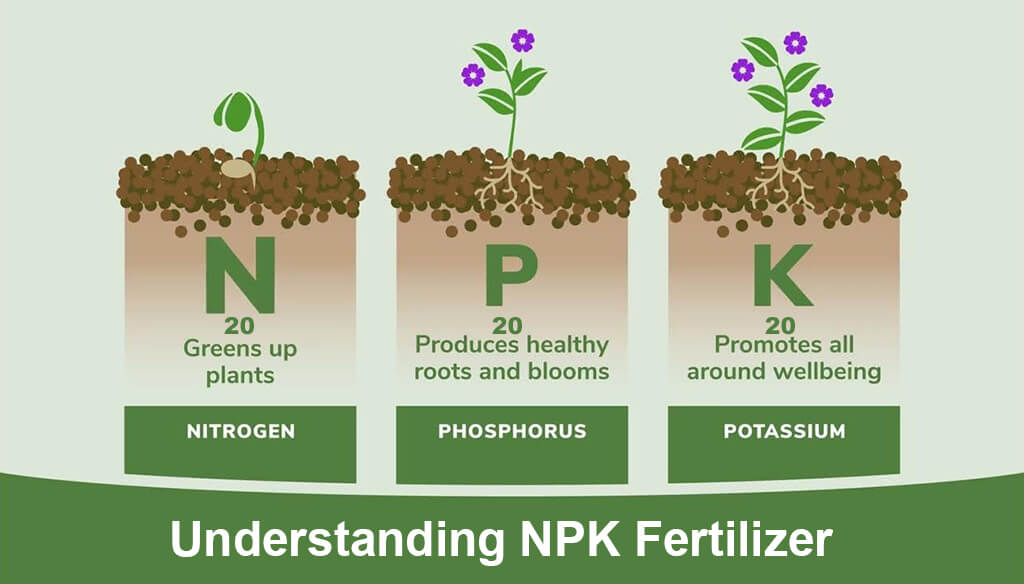
NPK fertilizers are formulated with specific ratios of Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K). These ratios are essential for meeting the nutritional requirements of various crops.
Nitrogen (N): Typically represented as the first number in the NPK ratio, nitrogen is crucial for promoting leafy growth. It supports the synthesis of amino acids, proteins, and chlorophyll, essential for photosynthesis.
Phosphorus (P): The second number in the NPK ratio, phosphorus is vital for root development and energy transfer within the plant. It is particularly important during the flowering and fruiting stages.
Potassium (K): The last number in the NPK ratio, potassium enhances overall plant health by regulating water uptake, improving drought resistance, and increasing disease resistance. It also plays a key role in fruit quality and yield.
Example Ratios:
- Conventional NPK Ratios: For example 10-20-10, has 10% nitrogen, 20% phosphorus, and 10% potassium, making it suitable for flowering plants that require higher phosphorus.
2. Soil Testing
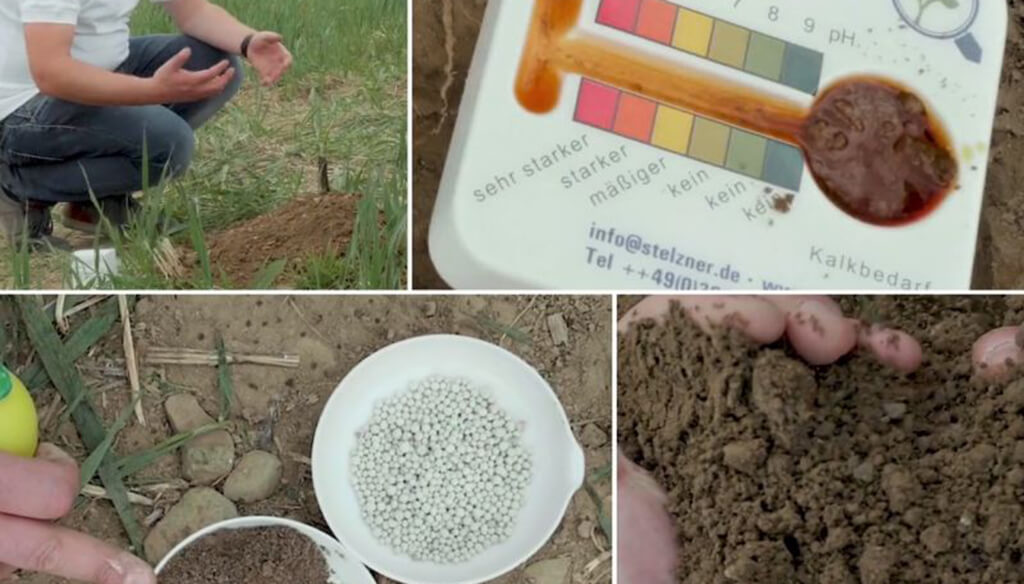

Conducting a thorough soil test is crucial for determining the nutrient content and pH of your soil.
How to Test Soil:
- Sample Collection: Take soil samples from multiple locations in your garden or field to get a representative sample.
- Testing Methods: Use a home testing kit, or send samples to a professional lab for detailed analysis.
- Analyze Results: Look for nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium levels, and pH. This information will guide your choice of NPK fertilizer.
Interpreting Soil Test Results:
- If nitrogen levels are low, consider a fertilizer with a higher nitrogen ratio.
- Low phosphorus levels may require a higher middle number in the NPK ratio.
- Adjust potassium levels based on your crop’s specific requirements.
3. Application Methods

Understanding when to use NPK fertilizers and how to apply them ensures effective nutrient delivery.
A. Broadcasting
- When to Use: Best for pre-planting or early season applications.
- How to Apply:
- Spread the fertilizer evenly over the soil surface.
- Use a spreader for large areas or apply by hand for smaller plots.
- Incorporate into the top 2-4 inches of soil to improve nutrient availability.
B. Side-Dressing
- When to Use: During the growing season, especially for nitrogen-demanding crops.
- How to Apply:
- Create a shallow furrow alongside the plant rows.
- Apply the recommended rate of fertilizer and gently cover it with soil.
- Water after application to help nutrients reach the root zone.
C. Drip Irrigation (Fertigation)
- When to Use: Ideal for precision agriculture and water conservation.
- How to Apply:
- Dilute NPK fertilizer according to product instructions.
- Inject the solution into the irrigation system, ensuring uniform distribution to plant roots.
D. Foliar Application
- When to Use: For quick nutrient uptake, especially during flowering or when deficiencies are suspected.
- How to Apply:
- Prepare a diluted solution of NPK fertilizer.
- Spray on the foliage in the early morning or late afternoon to avoid leaf burn.
- Ensure thorough coverage of leaves for maximum absorption.
4. Recommended Application Rates
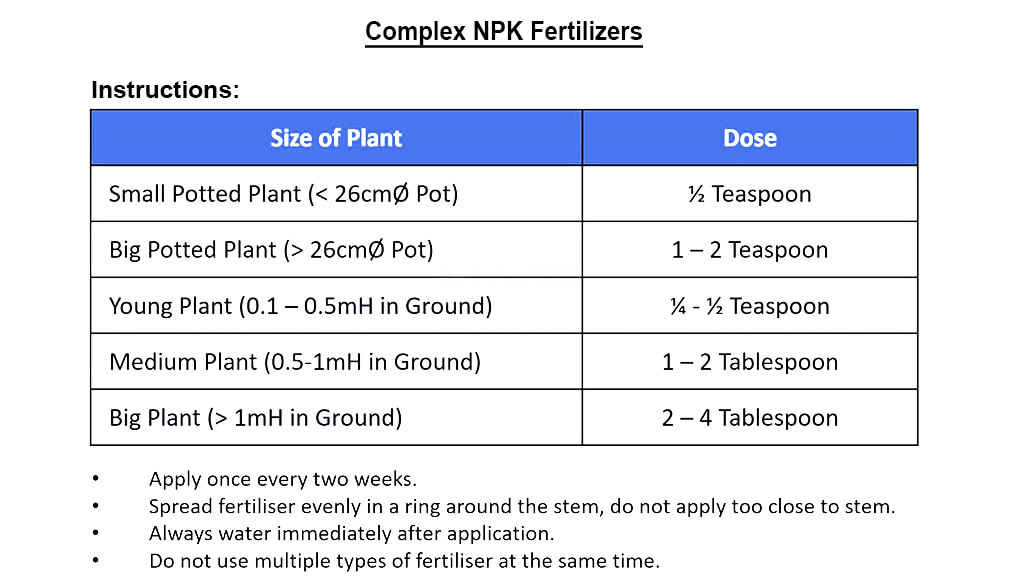
Accurate application rates are crucial for preventing nutrient imbalances:
General Guidelines:
- For granular fertilizers, apply approximately 1-2 pounds per 100 square feet, adjusting based on soil test results.
- For liquid fertilizers, dilute according to manufacturer instructions and apply every 4-6 weeks during the growing season.
Crop-Specific Recommendations:
- Leafy Greens: High nitrogen ratios (e.g., 20-10-10) to promote leafy growth.
- Root Vegetables: Balanced ratios (e.g., 10-10-10) for overall development.
- Fruit-Bearing Plants: Higher phosphorus and potassium (e.g., 5-20-20) to enhance flowering and fruit quality.
5. Timing of Application
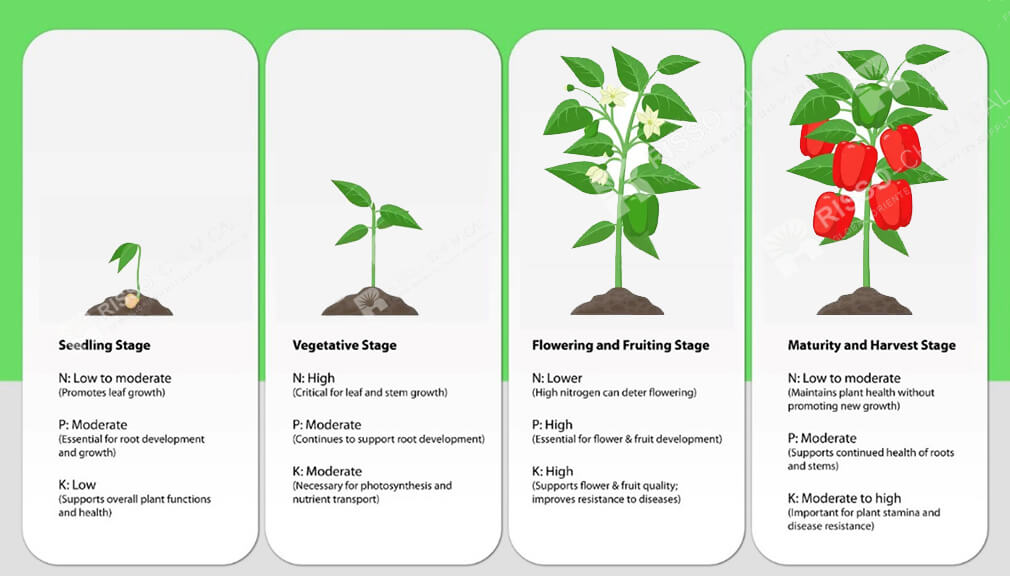
The timing of fertilizer application significantly impacts its effectiveness:
Pre-Planting: Apply NPK fertilizers before planting to establish nutrient reserves in the soil.
During the Growing Season:
- For fast-growing crops, side-dress with nitrogen after the plants are established.
- Adjust applications based on growth stages—more nitrogen during vegetative growth and more phosphorus and potassium during flowering and fruiting.
Late Season: Avoid high nitrogen applications late in the growing season to prevent excessive foliage growth at the expense of fruit and flower development.
6. Monitoring and Adjusting
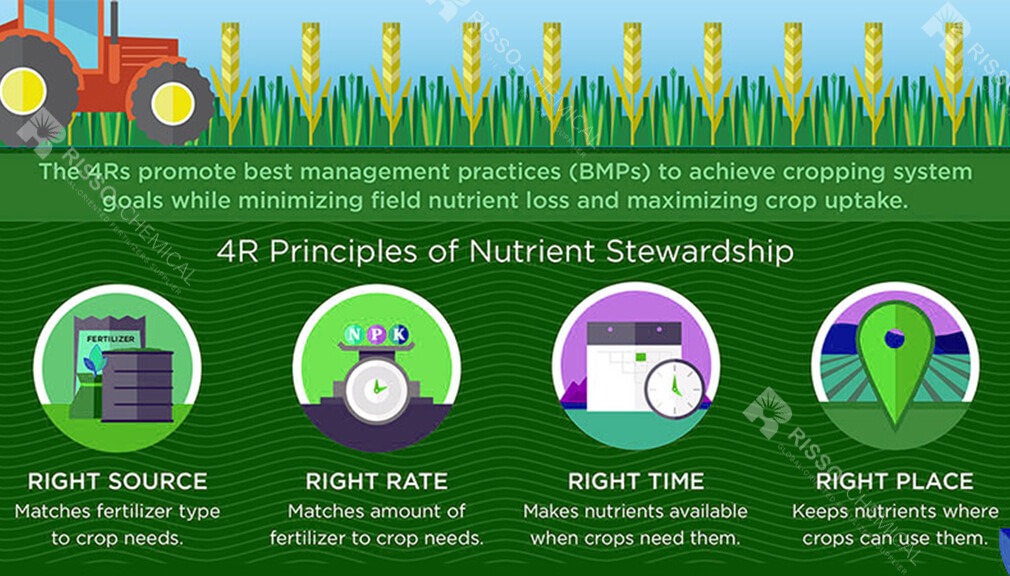
Regular monitoring of plant health and soil conditions allows for timely adjustments:
Visual Inspections: Regularly check for signs of nutrient deficiencies or excesses, such as:
- Yellowing leaves (nitrogen deficiency)
- Poor root development (phosphorus deficiency)
- Leaf burn or wilting (nutrient overload)
Soil Testing: Re-test soil every 1-2 years to assess changes in nutrient levels and pH.
Adjust Fertilization Strategies: Based on observations and soil test results, modify your fertilizer application as needed to optimize plant health.
7. Environmental Considerations
To minimize environmental impact and promote sustainability:
Prevent Runoff: Avoid applying fertilizers before heavy rains to reduce the risk of nutrient leaching into waterways.
Use Slow-Release Formulations: Consider slow-release fertilizers to provide a steady supply of nutrients over time, reducing the risk of nutrient spikes and environmental harm.
Implement Buffer Zones: Establish buffer zones with cover crops or grass strips around fields to absorb excess nutrients and prevent runoff.
Conclusion
Effective use of NPK compound fertilizers involves understanding nutrient needs, soil conditions, and precise application methods. By following these detailed instructions, you can ensure optimal plant health and productivity while promoting sustainable agricultural practices. For tailored solutions, explore Risso Fertilizer’s range of the Best NPK Fertilizer products designed to meet diverse crop requirements.
Fertilizer Related Products
If you want to know other questions about using NPK fertilizers or NPK fertilizers , please contact us and we will provide professional answers.
- Article
What will you get when touch?
✔ Quick & helpful reply within 6 hours.
✔ Tailored solutions for your project.
✔ One-stop product, tech, market
TRENDING
Want to find a China fertilizer manufacturer?
Risso will be your best choice; send us your request for your fertilizer details requirement
TAIAN RISSO CHEMICAL FERTILIZER CO.,LTD.
- Address: High-tech Development Zone, Taian City, Shandong Province
© Copyright 2017 RISSO CHEMICAL. All Rights Reserved.











