Let more growers get greater benefits
Industrial Urea vs Feed Grade Urea: Key Differences & Uses
- Industry News
- February 3, 2026
- 2:51 pm


Risso supplies reliable nitrogen solutions for agriculture and animal nutrition worldwide. Understanding the differences between industrial urea and feed grade urea is essential for selecting the correct nitrogen source for crop fertilization, industrial processing, or ruminant feed applications.
Although both products share the same chemical formula, their quality standards, impurity control, and safety regulations differ significantly.
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Urea and Nitrogen Function1. Introduction to Urea and Nitrogen Function
- 2. What Is Industrial (Fertilizer) Urea?2. What Is Industrial (Fertilizer) Urea?
- 3. What Is Feed Grade Urea?3. What Is Feed Grade Urea?
- 4. Soil pH, Ammonia Volatilization, and Nitrogen Use Efficiency4. Soil pH, Ammonia Volatilization, and Nitrogen Use Efficiency
- 5. Safety, Regulatory Compliance & Quality Control5. Safety, Regulatory Compliance & Quality Control
- 6. Application Scenarios and Practical Uses6. Application Scenarios and Practical Uses
- 7. How to Choose the Right Urea Grade7. How to Choose the Right Urea Grade
- 8. Summary and Professional Recommendations8. Summary and Professional Recommendations
1. Introduction to Urea and Nitrogen Function
2. What Is Industrial (Fertilizer) Urea?
Typical Applications
- Nitrogen fertilizer for crops and soils
- Raw material for compound fertilizers
- Chemical manufacturing and industrial processing
Typical Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Industrial Urea |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen Content | ~46% |
| Purity | ≥99% |
| Moisture | ≤0.5% |
| Biuret | Not strictly controlled |
| Additives | Anti-caking agents may be present |
| Intended Use | Non-feed applications only |
3. What Is Feed Grade Urea?
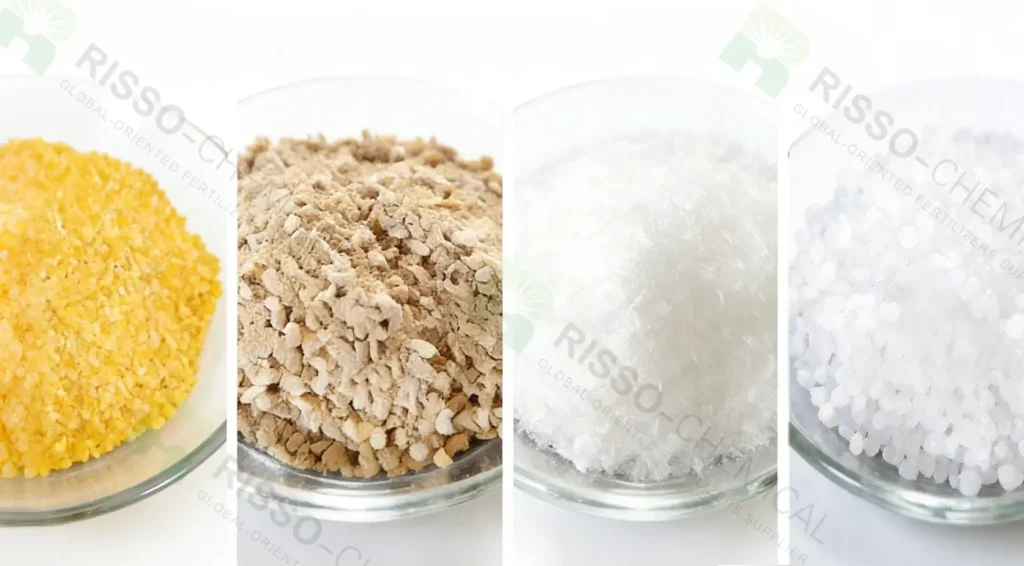


Appearance of Feed Grade Urea
Yellow granules, white crystals, or light brown flakes (blended with corn stalk residue)
This controlled appearance reflects uniform particle size, good flowability, and stable mixing performance, making feed grade urea suitable for inclusion in TMR, premixes, and mineral blocks.
Key Technical Parameters
| Parameter | Feed Grade Urea |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | CO(NH₂)₂ |
| Nitrogen Content | ≥46% |
| Biuret Content | ≤1.0% |
| Moisture | ≤0.5% |
| Heavy Metals | Strictly limited |
| Particle Form | Granules, crystals, or flakes |
| Documentation | COA & batch traceability |
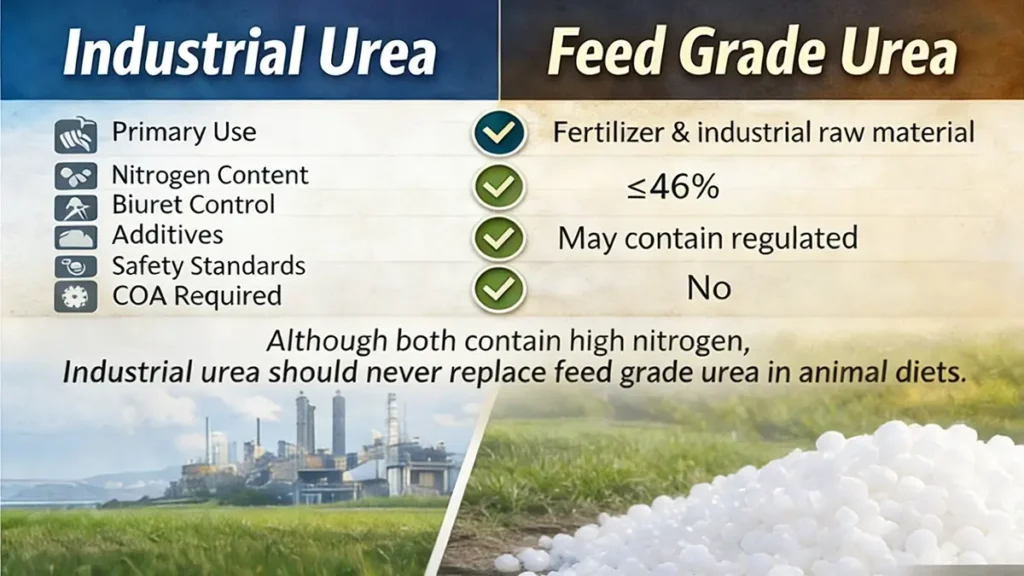
4. Industrial Urea vs Feed Grade Urea: Key Differences
| Feature | Industrial Urea | Feed Grade Urea |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Fertilizer & industrial raw material | Ruminant feed supplementation |
| Nitrogen Content | ~46% | ~46% |
| Biuret Control | Not strictly regulated | ≤1% |
| Additives | May contain conditioners | Feed-safe formulation |
| Safety Standards | Fertilizer regulations | Feed additive regulations |
| COA Required | Yes | Yes |
| Animal Feed Use | Not allowed | Designed for livestock |
5. Safety, Regulatory Compliance & Quality Control


Ruminants can utilize urea efficiently, while non-ruminant animals such as pigs and poultry cannot, making proper grade selection critical for feed safety.
Risso follows strict quality management practices to ensure consistent nitrogen content, low biuret levels, and reliable batch stability.6. Application Scenarios and Practical Uses
Industrial Urea
- Crop fertilization and soil nutrition
- Fertilizer blending and industrial processing
- Chemical raw material applications
Feed Grade Urea
- Non-protein nitrogen source for cattle and sheep
- Inclusion in TMR, feed premixes, and mineral blocks
- Improving feed efficiency and reducing protein costs
7. How to Choose the Right Urea Grade
- Agricultural or industrial use → Industrial urea
Cattle, sheep, or goat feed → Feed grade urea with verified COA
Always follow recommended inclusion rates and professional nutrition guidance

8. Summary and Professional Recommendations
Industrial urea is optimized for crops and industrial processes
Feed grade urea is engineered for safe and efficient ruminant nutrition
Correct selection ensures animal health, feed efficiency, regulatory compliance, and cost-effective nitrogen utilization. Risso provides dependable urea solutions for both agricultural and feed applications, supporting sustainable production worldwide.
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Feed grade urea is a high-purity urea designed for animal nutrition as a non-protein nitrogen source for ruminants like cattle, sheep, and goats. Industrial urea has the same chemical formula but is produced for fertilizer and industrial use, with impurity levels and additives unsuitable for livestock feed.
Feed grade urea provides concentrated non-protein nitrogen, which rumen microbes convert into microbial protein. This supports digestion, feed efficiency, and animal performance when included at proper levels in TMR, premixes, or mineral blocks.
Biuret is a urea by-product that can reduce palatability and interfere with microbial protein synthesis if excessive. Feed grade urea limits biuret to ≤1% to maintain rumen health and digestion efficiency.
Feed grade urea is an economical nitrogen supplement that can partially replace high-cost protein ingredients such as soybean meal. It supports microbial protein synthesis, reduces feed costs, and maintains ruminant growth and milk production.
Introduce urea gradually and adhere to recommended inclusion rates. Combine it with fermentable carbohydrates to optimize rumen microbial activity and prevent ammonia toxicity, ensuring safe and efficient nitrogen utilization.
Urea Fertilizer related products
If you want to know other questions about Urea, please contact us and we will provide professional answers.
- Article
What will you get when touch?
✔ Quick & helpful reply within 6 hours.
✔ Tailored solutions for your project.
✔ One-stop product, tech, market
TRENDING
Want to find a China fertilizer manufacturer?
Risso will be your best choice; send us your request for your fertilizer details requirement
TAIAN RISSO CHEMICAL FERTILIZER CO.,LTD.
- Address: High-tech Development Zone, Taian City, Shandong Province
© Copyright 2017 RISSO CHEMICAL. All Rights Reserved.











