Let more growers get greater benefits
Conventional NPK Ratios in Fertilizers
- Industry News
- April 9, 2024
- 1:54 pm

When it comes to optimizing plant growth, understanding the conventional ratios of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) in fertilizers is essential. These three macronutrients are critical for various physiological processes, and A balanced application of either type of NPK fertilizer can significantly impact crop yield and health.
List of Contents
What Do the Numbers Mean?
The NPK ratio is expressed as three numbers on fertilizer packaging (e.g., 10-10-10 or 12-24-12). Each number represents the percentage of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, respectively. Here’s a closer look at the roles of each nutrient:
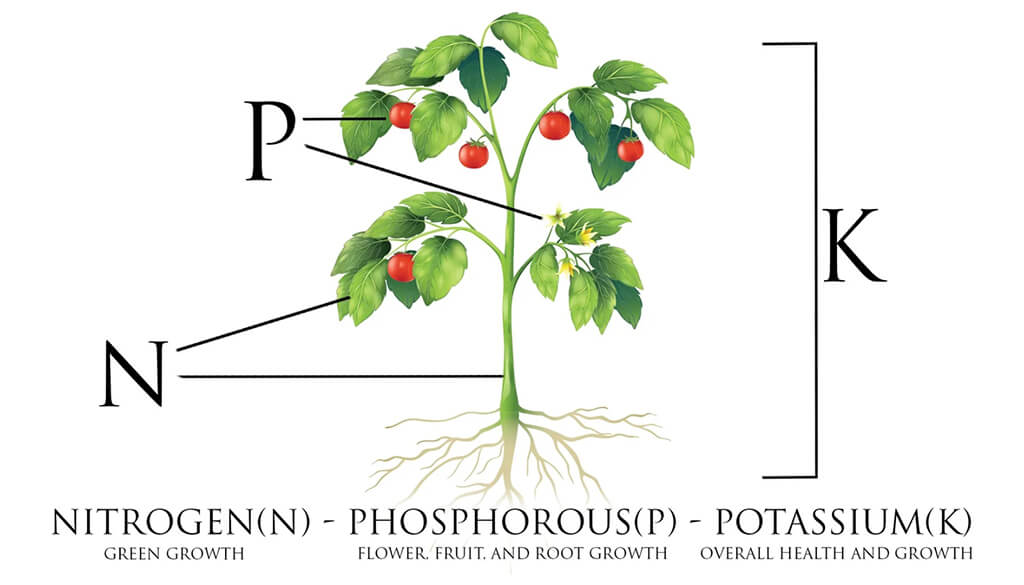
Nitrogen (N): Crucial for leafy growth and overall plant vigor, nitrogen promotes lush, green foliage and is a key component of chlorophyll.
Phosphorus (P): Important for root development, flowering, and fruiting, phosphorus aids in energy transfer and photosynthesis.
Potassium (K): Enhances overall plant health, disease resistance, and water regulation. Potassium is vital for flower and fruit quality.
Conventional NPK Ratios

| NPK 5-5-5 | NPK 9-9-9 | NPK 10-10-10 | NPK 12-12-12 |
| NPK 13-13-13 | NPK 14-14-14 | NPK 15-15-15 | NPK 16-16-16 |
| NPK 17-17-17 | NPK 19-19-19 | NPK 20-20-20 | NPK 21-21-21 |
High Nitrogen Ratios (20-10-10 or 30-10-10): These fertilizers are formulated to promote leafy growth and are ideal for leafy vegetables, such as lettuce and spinach, as well as for lawns. The higher nitrogen content encourages lush, green foliage, making them perfect for promoting vigorous vegetative growth.
| NPK 20-5-5 | NPK 20-10-10 | NPK20-12-12 | NPK 25-6-10 |
| NPK 30-5-5 | NPK 30-10-10 | NPK 30-9-20 | Ratio customization |
High Phosphorus Ratios (10-52-10 or 12-24-12): Best used during the planting phase or for flowering plants, these fertilizers encourage strong root development and flowering. They are particularly beneficial for bulbs, perennials, and fruit-bearing plants, helping to ensure a robust flowering and fruiting period.
| NPK 10-26-0 | NPK 11-22-16 | NPK 12-24-12 | NPK 10-52-10 |
| NPK 10-25-19 | NPK 12-25-10 | NPK 15-25-10 | Ratio customization |
High Potassium Ratios (12-12-17 or 15-5-32): These formulations are effective during the flowering and fruiting stages, improving fruit quality and enhancing disease resistance. They are ideal for tomato, pepper, and flowering plants, where potassium plays a crucial role in developing strong stems and vibrant blooms.
| NPK 5-10-20 | NPK 10-10-20 | NPK 10-12-30 | NPK 10-15-20 |
| NPK 12-6-22 | NPK 15-5-20 | NPK 15-5-32 | Ratio customization |
Specialized Ratios: Some NPK fertilizers are designed for specific plant types or growth stages, like 15-30-15 for blooming plants or 8-4-24 for fruiting crops. Understanding the specific needs of your plants can help you select the right specialized fertilizer for optimal growth.
| NPK 15-15-8 | NPK 13-27-27 | NPK 16-16-8 | NPK 20-10-20 |
| NPK 20-20-0 | NPK 26-6-26 | NPK 26-10-26 | Ratio customization |
Choosing the Right Ratio
Selecting the appropriate NPK ratio depends on several factors:
Plant Type: Different plants have varying nutrient needs. Leafy greens thrive on higher nitrogen, while flowering plants benefit from more phosphorus.
Growth Stage: Nutrient requirements change throughout the growth cycle. Seedlings require more phosphorus for root development, while fruiting plants need potassium to enhance fruit quality.
Soil Nutrient Levels: Conducting a soil test can provide valuable insights into existing nutrient levels. This information can help guide your choice of fertilizer, ensuring you provide the right nutrients without over-fertilizing.
Application Tips
Timing: Apply fertilizers at the right time, such as during planting or when plants are actively growing.
Method: Use appropriate application methods—broadcasting, side dressing, or foliar feeding—depending on the fertilizer type and plant needs.
Watering: Water after applying NPK fertilizers to help dissolve them and facilitate nutrient uptake.
Conclusion
Understanding conventional NPK ratios is crucial for effective fertilization. By selecting the right fertilizer based on the specific needs of your plants, you can promote healthy growth, improve yields, and ensure a thriving garden or agricultural operation. Whether you’re growing vegetables, flowers, or turf, the right NPK ratio can make all the difference in achieving your gardening goals.
TRENDING
Want to find a China fertilizer manufacturer?
Risso will be your best choice; send us your request for your fertilizer details requirement.
TAIAN RISSO CHEMICAL FERTILIZER CO.,LTD
- Address: No. 3168 Taishan Street, Tai'an City, Shandong Province.
© Copyright 2017 RISSO CHEMICAL. All Rights Reserved.






