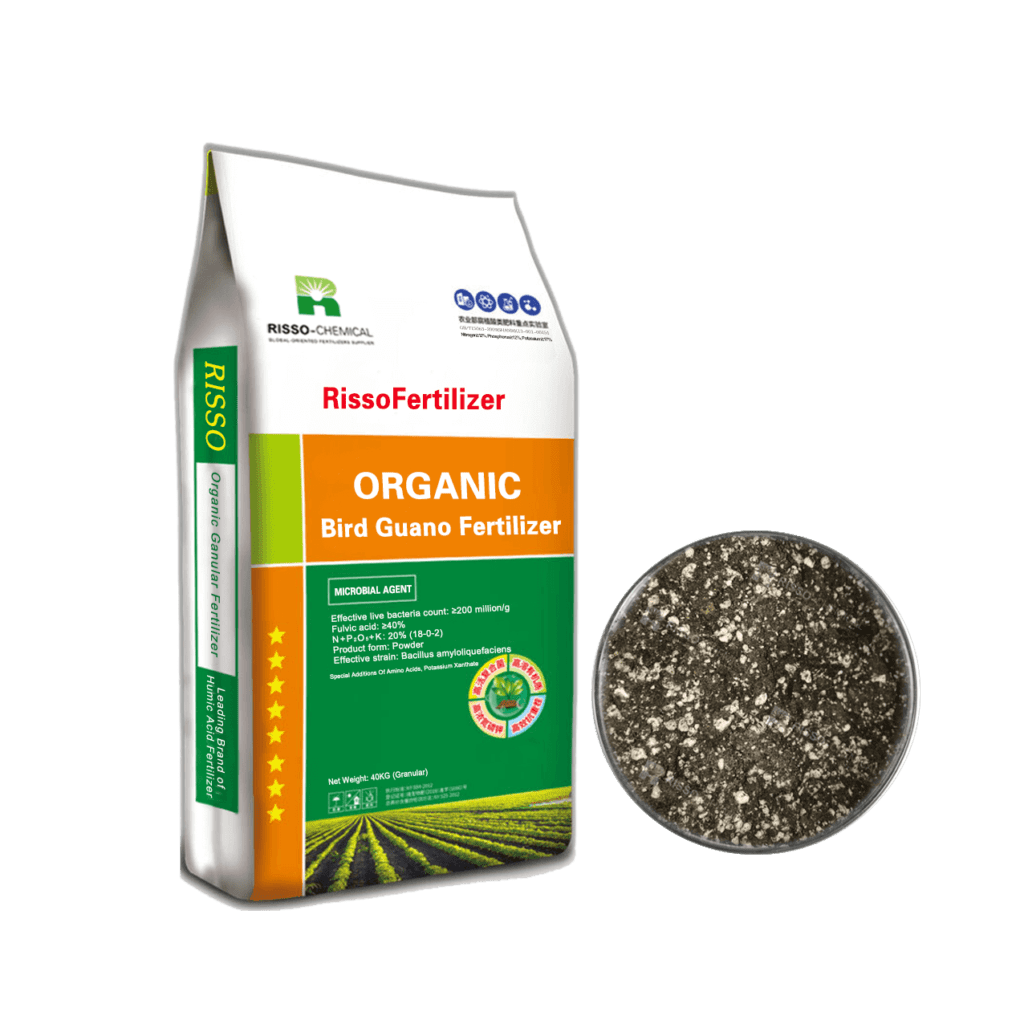
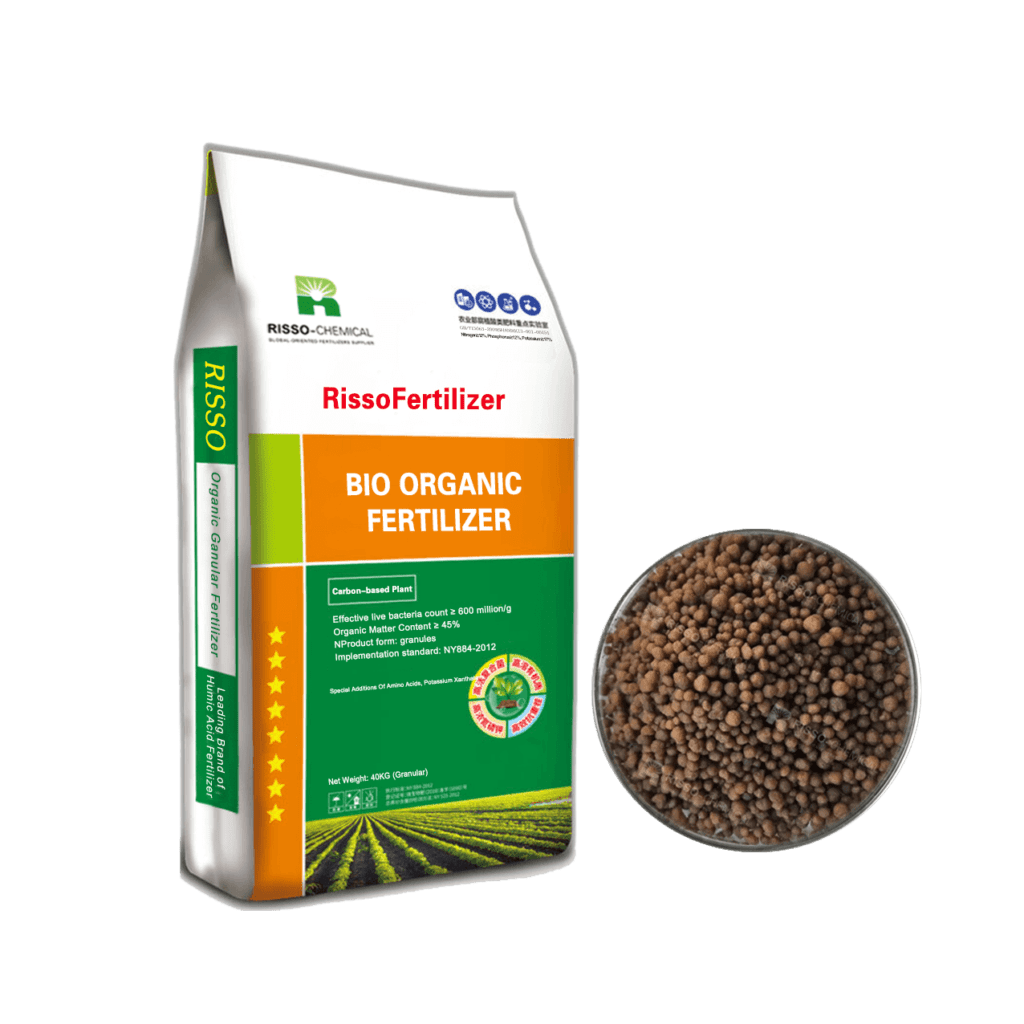
Let more growers get greater benefits
Comprehensive Guide to Types of Organic Fertilizers
- Industry News
- February 3, 2018
- 10:22 am
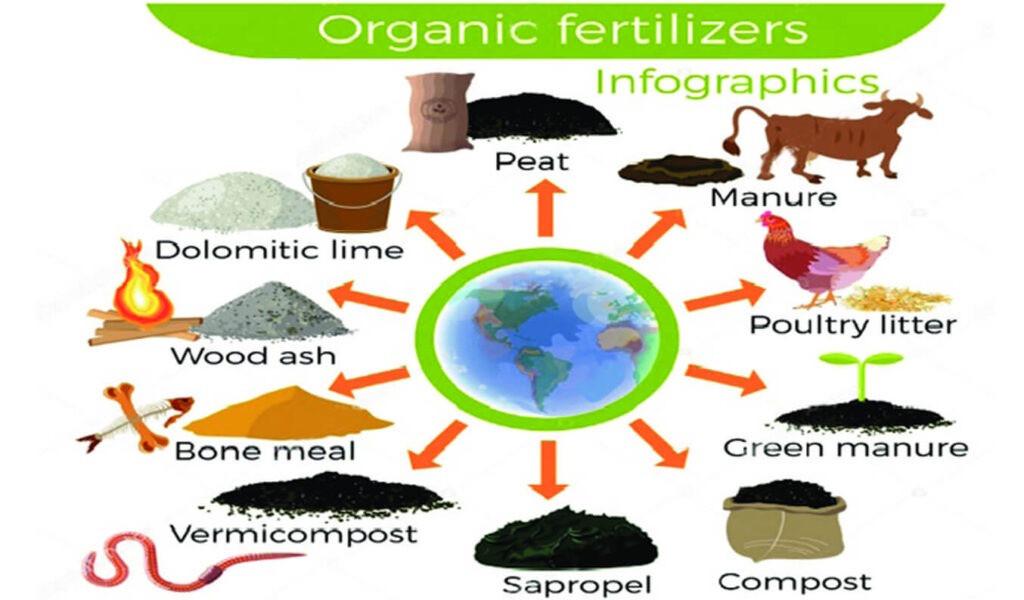
Organic fertilizers are a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture, offering an eco-friendly alternative to chemical fertilizers. They enrich the soil, improve its structure, and provide nutrients essential for plant growth. Organic fertilizers can be broadly categorized into animal-based, plant-based, mineral-based, and combined organic fertilizers. This article delves into each type, its subcategories, and its benefits.
Table of Contents
Animal-Based Organic Fertilizers
Animal-based fertilizers are derived from livestock, poultry, or marine animals, offering a rich source of macronutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Subcategories:
- Manure Fertilizer:
- Derived from livestock such as cows, horses, chickens, or sheep.
- Needs composting or aging to prevent pathogens and nutrient burn.
- Rich in nitrogen and organic matter.
- Bone Meal:
- Made from crushed animal bones.
- High in phosphorus and calcium, promoting strong roots and blooms.
- Blood Meal:
- A nitrogen-rich byproduct of slaughterhouses.
- Encourages lush, green foliage.
- Fish Emulsion and Fish Meal:
- Liquid or powdered fertilizers made from fish waste.
- Provides a balanced nutrient profile and trace minerals.
Key Benefits:
- Promotes vigorous plant growth.
- Enhances microbial activity in the soil.
- Boosts the soil’s water-retention ability.
Plant-Based Organic Fertilizers
Plant-based fertilizers are derived from decomposed or processed plant materials. They release nutrients slowly and improve soil structure.
Subcategories:
- Compost:
- Made from decomposed organic matter such as vegetable scraps, leaves, and garden waste.
- Improves soil health and encourages microbial diversity.
- Green Manures:
- Cover crops like clover or rye are grown and plowed into the soil.
- Adds organic matter and nitrogen.
- Seaweed Extract:
- Provides potassium, trace elements, and plant hormones.
- Used as liquid extracts or dried powders.
Key Benefits:
- Supports soil aeration and structure.
- Encourages healthy root systems.
- Contains natural growth-promoting substances.
Mineral-Based Organic Fertilizers
Subcategories:- Rock Phosphate:
- Supplies phosphorus for flowering and fruiting plants.
- Best suited for acidic soils.
- Greensand:
- A source of potassium and trace minerals like iron and magnesium.
- Improves soil water retention.
- Gypsum:
- Contains calcium and sulfur.
- Helps loosen compacted soils and improve drainage.
Key Benefits:
- Balances soil pH levels.
- Slowly releases nutrients over time.
- Supplies essential micronutrients often missing in soils.
- Supplies phosphorus for flowering and fruiting plants.
- Best suited for acidic soils.
- A source of potassium and trace minerals like iron and magnesium.
- Improves soil water retention.
- Contains calcium and sulfur.
- Helps loosen compacted soils and improve drainage.
Integrated Organic Fertilizers
Examples:- Organic Pellets or Granules:
- Combines manure, compost, and mineral additives.
- Convenient for broad application.
- Liquid Organic Blends:
- Mixes plant-based extracts, fish emulsions, and mineral solutions.
- Provides quick nutrient uptake for plants.
Key Benefits:
- Easy to apply.
- Customizable for specific soil and plant needs.
- Offers immediate and long-term nutrient release.
- Combines manure, compost, and mineral additives.
- Convenient for broad application.
- Mixes plant-based extracts, fish emulsions, and mineral solutions.
- Provides quick nutrient uptake for plants.
Specialty Organic Fertilizers
Specialty organic fertilizers are designed for targeted applications, such as improving soil microbes or addressing specific deficiencies.
Subcategories:
- Bio-Fertilizers:
- Contain live microorganisms like nitrogen-fixing bacteria and mycorrhizal fungi.
- Boost soil fertility and nutrient availability.
- Vermicompost:
- Produced by worms breaking down organic matter.
- Rich in enzymes, microbes, and nutrients.
Key Benefits:
- Enhances nutrient absorption efficiency.
- Promotes soil biodiversity.
- Reduces reliance on chemical fertilizers.
Choosing the right organic fertilizer is essential for healthy plant growth and soil improvement. Here are some key tips to help you make the best choice:
Know Your Soil: Test your soil to identify nutrient deficiencies and pH levels. This helps you choose a fertilizer that addresses specific needs.
Match Fertilizer to Plant Needs: Different plants have different nutrient requirements. For example, leafy vegetables need more nitrogen, while flowers and fruits need more phosphorus and potassium.
Choose the Right Form: Organic fertilizers come in liquid, granular, or powder form. Liquids are fast-acting, while granules and powders provide slow-release nutrients over time.
Consider Sustainability: Choose organic fertilizers that are locally sourced and eco-friendly. Organic options improve long-term soil health and reduce environmental impact.
Use a Combination: Sometimes, a mix of organic fertilizers—such as compost, manure, and bone meal—can provide a well-rounded nutrient boost.
By understanding your soil and plant needs, you can select the most effective organic fertilizer for healthy and thriving plants.
Conclusion
The diverse types of organic fertilizers offer solutions for every gardening and farming need. By selecting the appropriate fertilizer type and using it correctly, you can improve soil fertility, enhance plant health, and contribute to sustainable agricultural practices.
Whether you’re cultivating a home garden or managing a large-scale farm, organic fertilizers are a step toward a more eco-friendly and productive future.
Organic Fertilizers Related Products
If you want to know other questions about Organic fertilizers please contact us and we will provide professional answers.
- Article
What will you get when touch?
✔ Quick & helpful reply within 6 hours.
✔ Tailored solutions for your project.
✔ One-stop product, tech, market
TRENDING
Want to find a China fertilizer manufacturer?
Risso will be your best choice; send us your request for your fertilizer details requirement
TAIAN RISSO CHEMICAL FERTILIZER CO.,LTD.
- Address: High-tech Development Zone, Taian City, Shandong Province
© Copyright 2017 RISSO CHEMICAL. All Rights Reserved.











