Let more growers get greater benefits
Why Are NPK Fertilizer Prices So Expensive?
- Industry News
- August 7, 2017
- 3:00 pm
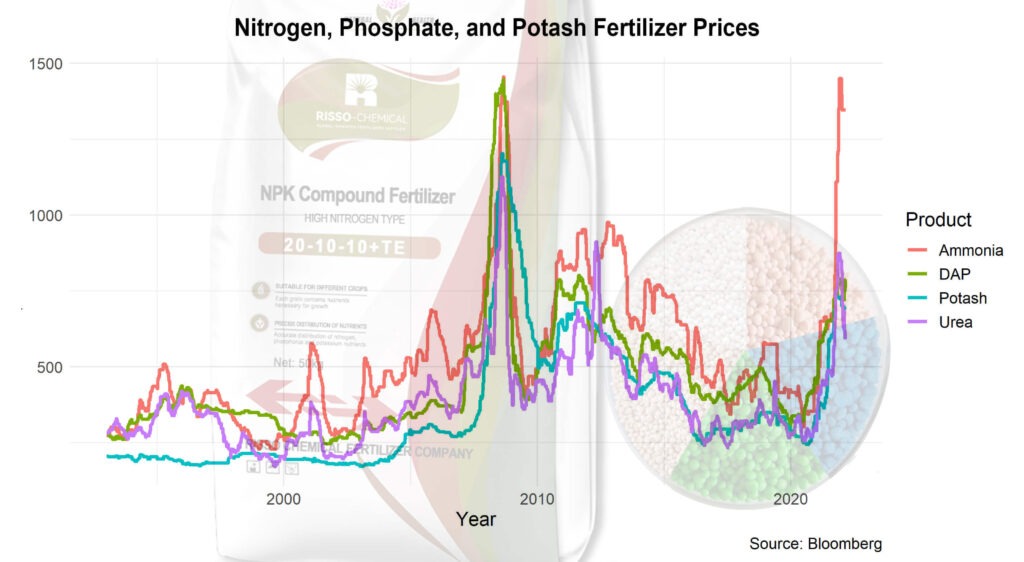

NPK fertilizers—composed of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K)—are essential for agricultural productivity worldwide. However, the prices of these fertilizers have seen steep increases in recent years, impacting farmers, food supply chains, and agricultural markets across the globe. In this blog, we’ll explore why NPK fertilizer prices are so high, examining the primary factors driving costs and the implications for the agricultural industry.
List of Contents
- 1. Global Demand and Increasing Food Production Needs
- 2. High Costs of Raw Materials: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium
- 3. Energy Costs and Production Expenses
- 4. Supply Chain Disruptions and Transportation Costs
- 5. Geopolitical Tensions and Trade Restrictions
- 6. Environmental Regulations and Sustainability Costs
- 7. Seasonal Demand and Weather-Related Impacts
- Implications for Farmers and the Agriculture Industry
- Future Outlook for NPK Fertilizer Prices
- Conclusion
1. Global Demand and Increasing Food Production Needs
The demand for NPK fertilizers has been steadily increasing due to rising global food consumption and the need for higher crop yields. As the world population grows, so does the demand for food, which drives the need for more efficient and productive agricultural practices. Farmers rely heavily on NPK fertilizers to ensure healthy crop growth and maximize yield, making these fertilizers a cornerstone of modern agriculture.
The increased demand, particularly in fast-growing economies such as China, India, and Brazil, has put pressure on the global supply of NPK fertilizers. This heightened demand has caused supply chain bottlenecks, which in turn have driven prices up.
2. High Costs of Raw Materials: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium


Each component of NPK fertilizers has its own production and pricing dynamics, and increases in these individual raw materials directly impact the final price of NPK fertilizers.
Nitrogen (N): Nitrogen fertilizers are often derived from ammonia, which is produced from natural gas. Therefore, nitrogen prices are closely tied to global natural gas prices. When natural gas prices rise, nitrogen prices also increase, making NPK fertilizers more expensive.
Phosphorus (P): Phosphorus is mined from phosphate rock, which is concentrated in specific regions, primarily Morocco, China, and the United States. Geopolitical tensions, export restrictions, and the limited number of suppliers make phosphorus susceptible to price volatility. Furthermore, extracting and processing phosphate rock is energy-intensive, adding to its production costs.
Potassium (K): Potassium is primarily sourced from potash mines in countries like Canada, Russia, and Belarus. Political issues or sanctions affecting any of these regions can disrupt supply chains and limit access to potassium, which drives up the cost of NPK fertilizers.
As raw material costs rise, NPK fertilizer manufacturers face increased production costs, which they pass on to the consumer.
3. Energy Costs and Production Expenses
The manufacturing process of NPK fertilizer is an energy intensive, especially for nitrogen-based fertilizers. The synthesis of ammonia (a key nitrogen source) requires significant amounts of energy, usually from natural gas. When energy prices rise, fertilizer production costs also increase. In recent years, global energy prices have surged, driven by factors such as geopolitical tensions, supply disruptions, and rising demand. As a result, the cost of producing NPK fertilizers has gone up, contributing to their higher market price.
4. Supply Chain Disruptions and Transportation Costs
The COVID-19 pandemic, coupled with subsequent geopolitical issues, has disrupted global supply chains, impacting the availability and cost of transporting fertilizers. Shipping delays, container shortages, and higher fuel prices have made it more expensive to transport both raw materials and finished fertilizers. In addition, disruptions at major ports and logistical bottlenecks have caused delays and increased costs throughout the fertilizer supply chain.
Higher transportation and logistics costs mean that manufacturers must pay more to move fertilizers from production facilities to agricultural regions, which ultimately raises the end price for consumers.
5. Geopolitical Tensions and Trade Restrictions
Geopolitical tensions play a significant role in fertilizer pricing. Several key suppliers of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are located in regions with complex political landscapes. For example, Russia and Belarus are major exporters of potash (potassium) and other essential fertilizer components. Political sanctions or export restrictions on these countries reduce global access to these materials, leading to price increases.
Additionally, trade policies, tariffs, and other regulatory measures can create further complications in the global fertilizer trade. For example, countries may impose tariffs on fertilizer exports to protect domestic supply, which can lead to shortages and price hikes in other regions.
6. Environmental Regulations and Sustainability Costs
With increasing awareness of the environmental impact of fertilizer production, governments and organizations are implementing stricter environmental regulations. Fertilizer manufacturing, particularly for nitrogen, produces significant emissions, which some countries are now regulating more rigorously. Compliance with environmental regulations often requires fertilizer companies to invest in cleaner technology and sustainable practices, adding to production costs.
While these regulations are essential for reducing pollution and preserving ecosystems, they contribute to higher production expenses, which are ultimately reflected in the price of NPK fertilizers.
7. Seasonal Demand and Weather-Related Impacts
NPK fertilizer demand often follows seasonal cycles aligned with planting and harvest periods. During peak planting seasons, demand for fertilizers increases, which can drive prices higher. Additionally, weather conditions, such as droughts, floods, or prolonged cold seasons, can impact planting schedules and fertilizer usage patterns. When weather conditions are favorable, demand may surge as farmers attempt to maximize crop production, leading to temporary price spikes.
Implications for Farmers and the Agriculture Industry
The rising cost of NPK fertilizers presents a significant challenge for farmers worldwide. For small-scale farmers or those in developing countries, high fertilizer costs can limit access to essential nutrients, impacting crop yields and overall food production. This can lead to higher food prices, impacting consumers and contributing to food insecurity in vulnerable regions.
Farmers may respond to higher fertilizer prices by adjusting their practices, such as:
- Precision Fertilization: Using soil testing and precision agriculture tools to apply fertilizers more efficiently, reducing waste and optimizing costs.
- Alternative Fertilizers: Exploring organic fertilizers, compost, and other alternatives to supplement NPK fertilizers and reduce dependency.
- Bulk Purchases and Contracts: Purchasing fertilizers in bulk or securing long-term contracts to lock in prices and avoid seasonal spikes.
Future Outlook for NPK Fertilizer Prices
Looking forward, NPK fertilizer prices will likely remain sensitive to factors like energy prices, raw material availability, and geopolitical issues. However, several trends may help stabilize prices over the long term:
- Technological Advancements: New methods in fertilizer production, such as green ammonia technology, may help reduce energy consumption and costs.
- Sustainable Practices: As the industry adapts to environmental regulations, more sustainable production practices could help offset compliance costs.
- Diversification of Supply Chains: By establishing diversified sources for raw materials and production facilities, the fertilizer industry may become more resilient to supply disruptions.
Conclusion


NPK fertilizer prices are high due to a complex web of factors, including increased global demand, raw material costs, energy prices, supply chain disruptions, geopolitical issues, and environmental regulations, (Prices are also related to the type of NPK fertilizer and the ratio of NPK). These cost drivers have made NPK fertilizers more expensive for farmers and agricultural sectors worldwide, impacting food production and, ultimately, consumers.
For now, the best approach for the agriculture industry is to embrace efficient, sustainable practices that optimize fertilizer use and reduce costs where possible. By understanding the factors influencing NPK fertilizer prices, farmers and distributors can make informed decisions to navigate the current market and continue fostering sustainable food production.
NPK Related Products
If you want to know other questions about NPK fertilizers or Blended fertilizers, please contact us and we will provide professional answers.
- Article
What will you get when touch?
✔ Quick & helpful reply within 6 hours.
✔ Tailored solutions for your project.
✔ One-stop product, tech, market
TRENDING
Want to find a China fertilizer manufacturer?
Risso will be your best choice; send us your request for your fertilizer details requirement
TAIAN RISSO CHEMICAL FERTILIZER CO.,LTD.
- Address: High-tech Development Zone, Taian City, Shandong Province
© Copyright 2017 RISSO CHEMICAL. All Rights Reserved.











